BBC
BBCBritain has pulled itself out of recession with the economy returning to growth in the first three months of the year, according to official figures.
Chancellor of the Exchequer Jeremy Hunt said the economy was “on the way to a full recovery”, but Labour's shadow chancellor Rachel Reeves said now was “not the time to celebrate victory”.
How do you measure the health of the economy?
The Office for National Statistics (ONS) publishes figures for the UK's Gross Domestic Product (GDP), which is the value of all the goods and services the UK produces.
When GDP rises, a country's economy grows, and as a result, average incomes rise.
But sometimes the economy contracts and GDP falls, which can be a sign of economic downturn and hit people's wallets.
What is a recession?
The UK is considered to be in recession if its GDP falls for two consecutive three-month periods.
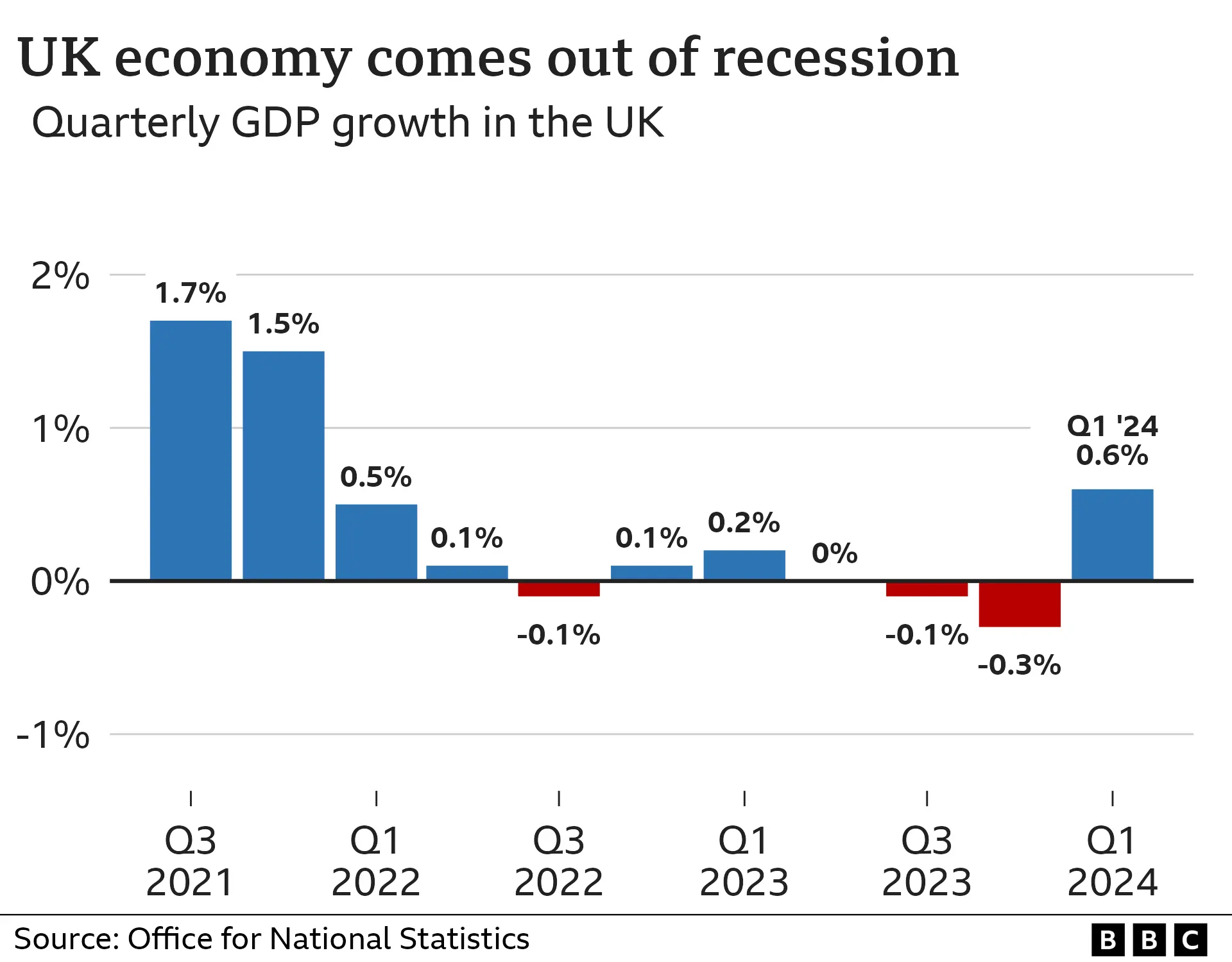
The economy contracted 0.1% from July to September last year and a further 0.3% from October to December.
However, the latest data from the Office for National Statistics shows the UK economy grew by 0.6% in the first three months of 2024, signalling an end to the recession.
When was the last UK recession and how long did it last?
The 20.4% decline in GDP recorded in April-June 2020 was the largest on record, but it only lasted six months.
In 2008, the global financial crisis triggered a recession that lasted for five quarters, or 15 months.
What happens in a recession and how will it affect me?
Economic growth creates more job opportunities and means businesses can pay out more profits to employees and shareholders.
Higher wages and increased profits also generate funds for the government through taxes.
These things could be reversed if the economy contracts and the country falls into recession.
 Getty Images
Getty ImagesPeople may lose their jobs and the unemployment rate may rise.
Others may find it harder to get promoted or get a big enough raise to keep up with inflation.
But the pain of a recession will not be felt equally across society, and inequalities may increase.
If the government decides to cut spending on public services, people on welfare and on fixed incomes in particular are likely to suffer.
How to get out of the recession?
This reduces borrowing costs for businesses and households, stimulating spending and economic growth.
When an economy struggles to grow but also has high inflation, a situation known as “stagflation” can occur.
This is very difficult to solve because the two problems require different solutions.
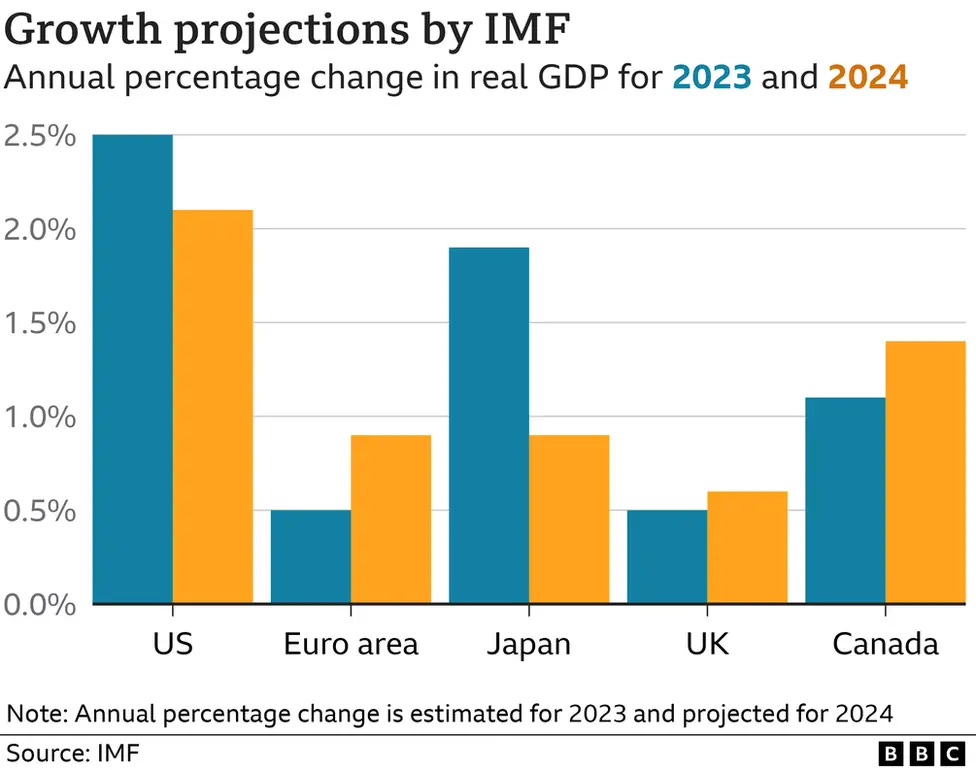
How does the UK economy compare to other countries?
But until then, the UK had been one of the weaker G7 countries.
This would give the US growth rate for the full year of 2023 a 2.5% growth rate, the best performance among other developed countries, and it is projected to outpace the rest of the G7 in 2024.