As your business grows and evolves, so do your business processes. Depending on the size of your company, there may be dozens, or even hundreds, of business processes that involve parties inside and outside your organization every day.
A business process consists of a set of steps that are executed in a specific order to achieve a desired result. The process can be dedicated to activities such as onboarding new clients, sales and marketing, customer support requests, order fulfillment, human resources, procurement management, accounting, etc.
As businesses and business environments change, these processes continually evolve and require continual evaluation, improvement, and optimization. Outdated processes can lead to customer and employee dissatisfaction, costly operational inefficiencies, and lost market share.
What is business process improvement and optimization?
Effective business process management (BPM) requires a well-thought-out plan that addresses the ongoing need to define, execute, evaluate, and iterate processes. At its core, BPM is about business process improvement and optimization — the operational practice of identifying, evaluating, and resolving business process problems and concerns.
The objective of business process improvement and optimization is to redesign existing processes to increase efficiency, streamline operations, upgrade communications, reduce errors and costs, and enhance workloads. These improvements should be made continuously as your business changes, evolves, expands, and implements new technologies.
There are several proven methodologies for improving and optimizing business processes: The following techniques and tools put the customer at the center of all your company’s operations.
- Six Sigma has been around since the mid-1980s as a popular approach to process improvement and total quality management. Six Sigma uses the concepts of DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) as a framework for continuous process improvement. This data-driven methodology focuses on improving processes through precise measurement and rigorous analysis, aiming for near-perfect performance.
- Lean thinking is a modification of Six Sigma. It focuses on specific tasks that provide more value to customers and identifies potential inefficiencies in processes. It identifies and eliminates non-value-added activities and streamlines operations to improve quality and efficiency. Lean principles go beyond manufacturing and are applied in various sectors, including services, to enhance processes by reducing waste, optimizing workflows, and delivering value to customers more efficiently.
- Total quality management (TQM) was popularized by manufacturers and government agencies in the 1980s. It focuses on eliminating defects in processes and improving the overall quality of the final product or service. TQM is a holistic approach that focuses on continuous improvement in all aspects of an organization's operations. In organizations that adopt TQM, all members participate in improving processes, products, services, and working culture.
Why are efficient business processes important?
Every business knows the value of efficient processes, but the reality is that many face workflow inefficiencies that need to be fixed. As companies undergo digital transformation in today's competitive business environment, inefficient processes can negatively impact a company's entire business operations. Even a single inefficient process can affect resources, workforce, profits, and the quality and reliability of products and services. Inefficient processes can create bottlenecks, impede operations, increase costs, miss deadlines and fail to complete tasks, and slow an organization's response to market fluctuations.
In a rapidly changing world, optimizing your business processes is not just a strategy, it's essential to survival and growth. Processes need to be constantly updated so that your organization isn't caught off guard. Organizations need to quickly adapt to the unprecedented pace of market changes, technological advancements, and evolving customer expectations.
Efficient, streamlined processes help organizations become agile and reduce time to market for new products and services to stay competitive. In addition, optimization often involves the integration of digital tools and technologies, leading to enhanced data analysis and decision-making capabilities. This digital transformation enables companies to predict market trends, improve customer experience, and continuously innovate. Flexible, optimized business processes are a key element of organizational agility.
However, keeping these processes up to date, improving them when necessary, and continually optimizing them can be difficult. People tend to resist change, especially when processes have been in place for a long time. It is important to communicate the purpose and benefits of improving business processes to stakeholders.
What are the benefits of optimizing business processes?
Well-managed and continuously improved processes can reduce errors, speed process completion times, enhance workload, identify waste, eliminate duplication, and improve overall business performance. Optimizing business processes improves consistency, quality, and compliance, reduces risk, and increases customer and management visibility.
Steps to improve and optimize business processes
When planning a business process improvement initiative, you determine your business objectives, where improvements are needed, and what items need to be optimized. A goal-centric vision provides the foundation for measuring and evaluating progress.
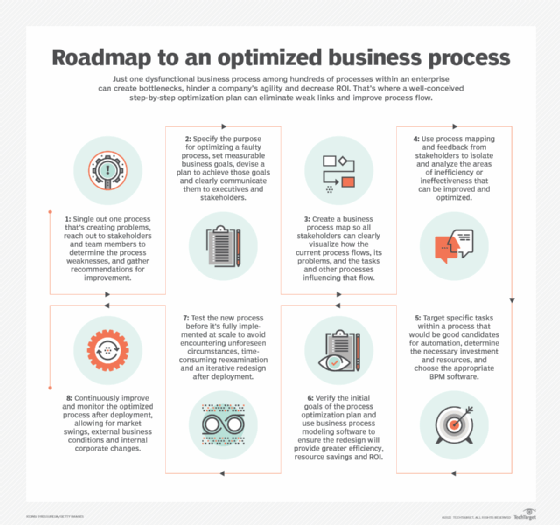
1. Identify one process that needs improvement.
Focus on one process that needs immediate improvement, reach out to stakeholders and team members to determine which tasks and activities are taking up the most time and resources, and gather recommendations on how to improve the process. Choose the tasks within that process that are the least complex and time-consuming to optimize and will provide an immediate ROI, regardless of size. Even small optimization projects can deliver big results, deliver quick wins for stakeholders, and help build company-wide buy-in for more complex process optimization activities.
2. Set business goals for your process improvement project
Once a process to improve has been identified, define the objectives for optimizing the process, set overall goals and smaller objectives that are immediately measurable, and develop a plan to achieve those goals. Have a clear understanding of what the optimization will achieve (for example, financial savings, resource savings, time savings, etc.). Clearly communicate these goals to executives and stakeholders so everyone is on board.
3. Map your existing processes
BPM and business process modeling techniques, popularized over the past decades, are used to visually map business processes. These tools help you define in an easy-to-understand and standardized way how your current processes flow through different departments, the different steps within the process, and which components in the process run sequentially or in parallel.
4. Analyze your current processes to identify weaknesses
Process mapping helps you analyze your current processes and find areas of inefficiency or ineffectiveness that can be improved and optimized. Using feedback provided by stakeholders, analyze which steps in your process take the most time, create bottlenecks, cause communication breakdowns, fail to deliver value, and can be reworked or removed. Optimization might include making some tasks conditional, consolidating certain tasks, adjusting data permissions, or automating manual tasks.
New AI-powered tools are beginning to emerge that can provide insight into which business processes may be bottlenecks and which processes could be optimized to improve profits.
5. Specific tasks to be automated
Automation provides an opportunity to rapidly improve and optimize business processes by removing manual bottlenecks, addressing repeatability and quality issues, and eliminating inefficiencies. Determine how much financial and time resources you have available to invest in business process automation software, and whether the necessary tools already exist within your organization.
6. Identify the initial goals of your process redesign plan
Ensure that your process redesign meets established business objectives and has a significant impact on process efficiency, resource savings, and ROI. Business process tools can help you model and measure the impact, and provide recommendations on where you can improve your processes during the pilot phase.
7. Test new processes before fully implementing them
Testing and quality assurance are equally important steps to ensure that new processes work before they are implemented on a large scale. Optimized business processes are often hindered by unforeseen circumstances. Testing the entire process before full implementation helps avoid post-deployment second thoughts and iterative redesign. Whether they are minor issues or major flaws, identifying these issues in a small-scale implementation helps organizations avoid the costly and time-consuming process of reevaluating and redesigning processes after they are already in place.
8. Continually improve and monitor the process after implementation
Once fully implemented, measure the efficiency and effectiveness of the new process. As market conditions and business operations change, business processes also change. Therefore, business processes require continuous evaluation and monitoring to ensure that they are delivering more value compared to the old process. Collect feedback from stakeholders and monitor the process for new pain points that need to be addressed.
Mastering Process Improvement and Optimization
Improving and optimizing business processes may seem like a daunting task, but it doesn't have to be. Starting with optimizing a single process, engaging stakeholders, and setting realistic, achievable goals increases the likelihood of success. Organizations that are willing to embrace change and continue to evolve their processes as their business grows and evolves will see significant benefits, including streamlined workflows, cost savings, increased operational efficiency, and improved customer and employee satisfaction.

